
of neutrons = 27 - 13 (atomic mass - number of protons) = 14

Similarly, the number of protons can be calculated if the mass number and number of neurons are given.įor example, Atomic mass of Aluminium = 27 We can calculate the number of neutrons if we have the mass number and number of protons of an element.

It means the atomic mass or mass of one atom of Magnesium is 24 times more than the 1/12 of the atomic mass of carbon 12.įrom the above relation between the mass number and protons and neutrons. So, we can say that the atomic mass of an element is the number of times its atom is heavier than 1/12 th of the mass of an atom of C-12, e.g., the atomic mass of Mg is 24 u. So, Atomic mass of an element = Mass number of one atom of the element (protons + neutrons) / (1/12) x mass of carbonįor example, atomic mass of oxygen in amu = 16 (8 proton + 8 neutron) / 1/12x 12 = 16 amu As of now amu is simply known as unified atomic mass and is written as 'u'. So, when we divide it into twelve parts, 1 amu is nearly equal to the 1 proton. There are 12 nucleons (protons + neutrons) in the nucleus of Carbon.

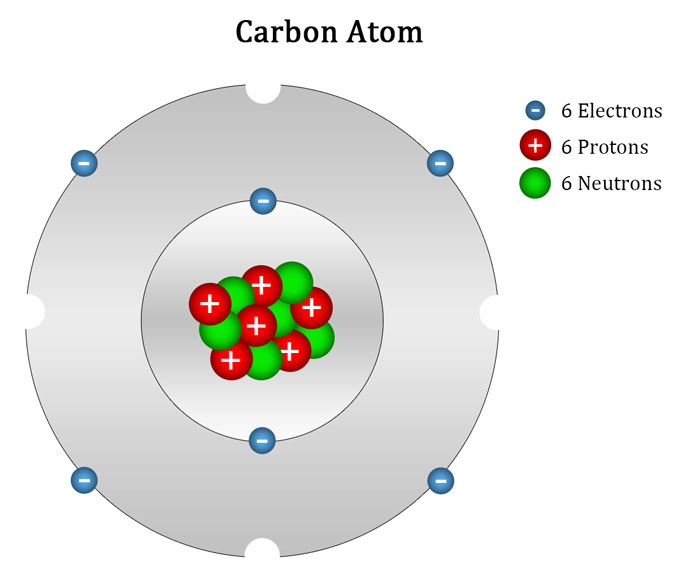
For example, if we divide C 12 atom into 12 equal pieces and take one piece then we can say that mass of this one piece is equal to 1 atomic mass unit, which is used as a standard to calculate the mass of any other atom. It is equal to one-twelfth (1/12) of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. The atomic mass unit is the unit to measure and represent the atomic mass. This way of representing atomic mass was not easy or appropriate, so to simplify the method or to assign an easy atomic mass figure, the concept of relative atomic mass was introduced by the scientists and a new unit called atomic mass unit (amu) was introduced to calculate the atomic mass of an atom. For example, the atomic mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.67 x 10 -27 kg. So, the mass of atoms is so small that it was difficult for the scientist to measure and represent its mass. The protons and neutrons that contribute to the atomic mass are present in the nucleus, which is present at the centre of the atom and its size is very small as compared to the atom. So, we can say that the atomic mass or mass number is equal to the total number of nucleons present in the atom of an element. The protons and neutrons are collectively known as nucleons as they are contained in the nucleus. So, we can say that the sum of all protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom is called its mass number. So, electrons are considered weightless.Ītomic mass is also referred to as the mass number. We can say that electrons do not contribute to the mass number of an atom as their mass is negligible as compared to the mass of a proton or a neutron. It does not include electrons as their weight is negligible as compared to protons and neutrons that have a significant amount of mass. It is the mass of a single atom of an element, which includes the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. The number of electrons may change as they take part in chemical reactions where an atom may lose or gain electrons. So, it is also the characteristic property of an element.įurthermore, the atomic number is always a whole number as the number of protons is fixed in an atom. The reactive capacity decides the properties of elements. So, atomic number acts as the identity of an element.īesides this, atomic number defines the characteristics or properties of an element as in a neutral atom, it is equal to the number of electrons, which determine the valency (reactive capacity) of an atom. Besides this, it is a unique number as two different elements cannot have the same number of protons, e.g., for example, oxygen has eight protons and no other element can have eight protons. All the atoms of an element contain the same number of protons. It is a number assigned to a particular element based on the number of protons present in its atoms. It is denoted by the letter Z of English. For example, Nitrogen has seven protons, so its atomic number is seven. The total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom is known as its atomic number. Next → ← prev Atomic Number & Atomic Mass | Mass Number Atomic Number


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
